Unveiling the Modern Periodic Table: A Comprehensive and Detailed Guide to Understanding Elements, Their Properties, and Periodic Classifications
Modern Periodic Law and the Present Form of the Periodic Table
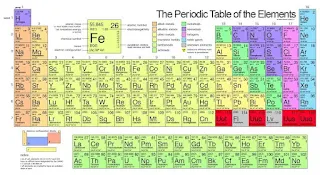
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table have undergone significant developments since the early attempts by scientists like Dmitri Mendeleev.
Early Developments
In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, developed the first periodic table. Mendeleev's table arranged elements in order of increasing atomic weight and recurring chemical properties. He predicted the existence of undiscovered elements and left gaps in the table for them.
Modern Periodic Law
The modern periodic law states that elements with similar properties and electron configurations recur at regular intervals when arranged in order of increasing atomic number. This law is based on the following principles:
1. Atomic Number: The atomic number of an element is the number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom.
2. Electron Configuration: The arrangement of electrons in an atom is determined by the atomic number.
3. Recurring Chemical Properties: Elements with similar electron configurations exhibit similar chemical properties.
Present Form of the Periodic Table
The present form of the periodic table is based on the modern periodic law. It consists of:
1. Periods: Horizontal rows of elements, arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
2. Groups: Vertical columns of elements, arranged in order of recurring chemical properties.
3. Blocks: Sections of the periodic table, based on the electron configuration of elements.
Key Features of the Periodic Table
1. Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids: The periodic table distinguishes between metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, based on their electron configurations and chemical properties.
2. Noble Gases: The noble gases, a group of unreactive elements, are placed in the far right column of the periodic table.
3. Lanthanides and Actinides: The lanthanides and actinides, two series of radioactive elements, are placed at the bottom of the periodic table.
Conclusion
The modern periodic law and the present form of the periodic table have revolutionized our understanding of the elements and their properties. By arranging elements in a logical and systematic order, the periodic table provides a powerful tool for predicting chemical behavior and identifying relationships between elements.
FAQs
1. What is the modern periodic law?
The modern periodic law states that elements with similar properties and electron configurations recur at regular intervals when arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
2. What is the present form of the periodic table?
The present form of the periodic table is based on the modern periodic law and consists of periods, groups, and blocks.
3. What are the key features of the periodic table?
The periodic table distinguishes between metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, and includes noble gases, lanthanides, and actinides.
References
1. Mendeleev, D. (1869). On the Relationship Between the Properties of the Elements and Their Atomic Weights.
2. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). (2016). Periodic Table of the Elements..
"This Content Sponsored by Buymote Shopping app
BuyMote E-Shopping Application is One of the Online Shopping App
Now Available on Play Store & App Store (Buymote E-Shopping)
Click Below Link and Install Application: https://buymote.shop/links/0f5993744a9213079a6b53e8
Sponsor Content: #buymote #buymoteeshopping #buymoteonline #buymoteshopping #buymoteapplication"
Comments
Post a Comment