Understanding Electronic Configurations: A Comprehensive Guide to spdf Blocks and Types of Elements in Chemistry
Here's a detailed explanation of electronic configurations and types of elements, including the SPDF blocks:
Understanding Electronic Configurations
Electronic configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom. It describes the distribution of electrons in different energy levels or shells around the nucleus. The electronic configuration of an element determines its chemical properties and behavior.
The Aufbau Principle and Pauli's Exclusion Principle
The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels in an atom. Pauli's exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers. These principles help us understand how electrons are arranged in an atom.
The Periodic Table and Electronic Configurations
The periodic table is arranged in a way that elements with similar electronic configurations are placed in the same group or period. Elements in the same group have the same number of electrons in their outermost energy level, which determines their chemical properties.
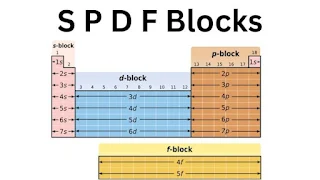
SPDF Blocks: Understanding the Types of Elements
The spdf blocks are a way of classifying elements based on their electronic configurations. The blocks are named after the types of orbitals that are occupied by the electrons.
s-Block Elements
- Electron Configuration: ns1-2 (where n is the principal quantum number)
- Properties: Typically, s-block elements are highly reactive metals with low ionization energies. They tend to lose electrons to form positive ions.
- Examples: Alkali metals (Group 1) and alkaline earth metals (Group 2)
p-Block Elements
- Electron Configuration: ns2 np1-6
- Properties: p-block elements exhibit a wide range of properties, from nonmetals to metals. They can form ions with different charges and exhibit variable valency.
- Examples: Halogens (Group 17), noble gases (Group 18), and post-transition metals
d-Block Elements
- Electron Configuration: (n-1)d1-10 ns0-2
- Properties: d-block elements are typically metals with high melting points and densities. They exhibit variable valency and can form ions with different charges.
- Examples: Transition metals (Groups 3-12)
F-Block Elements
- Electron Configuration: (n-2)f1-14 (n-1)d0-1 ns2
- Properties: f-block elements are typically radioactive, metallic elements with high melting points. They exhibit variable valency and can form ions with different charges.
- Examples: Lanthanides (inner transition metals) and actinides
In conclusion, understanding electronic configurations and the spdf blocks is crucial for explaining the properties and behavior of elements. By knowing how electrons are arranged in an atom, we can predict an element's chemical properties, reactivity, and behavior under different conditions.
"This Content Sponsored by Buymote Shopping app
BuyMote E-Shopping Application is One of the Online Shopping App
Now Available on Play Store & App Store (Buymote E-Shopping)
Click Below Link and Install Application: https://buymote.shop/links/0f5993744a9213079a6b53e8
Sponsor Content: #buymote #buymoteeshopping #buymoteonline #buymoteshopping #buymoteapplication"
Comments
Post a Comment